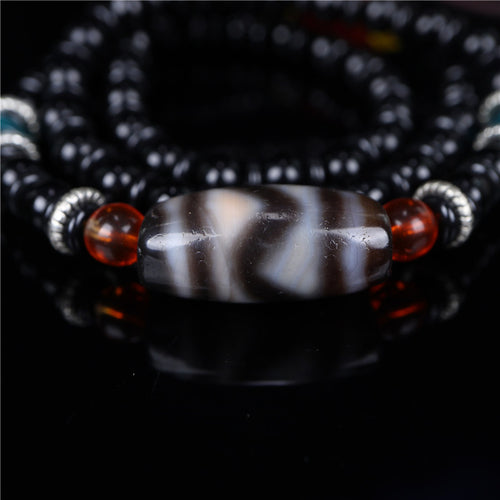
Yes, Buddha, also known as Siddhartha Gautama, shared numerous teachings about happiness, life, and the nature of existence. Some key concepts from his teachings include:
Four Noble Truths: Buddha articulated the Four Noble Truths, which form the foundation of his teachings. They revolve around the nature of suffering (dukkha), the causes of suffering (samudaya), the cessation of suffering (nirodha), and the path leading to the cessation of suffering (magga).
Middle Way: Buddha advocated for the Middle Way, emphasizing a balanced approach between extreme self-indulgence and extreme asceticism. He taught that true happiness and enlightenment come from finding a balanced and moderate path in life.
Impermanence and Change: Buddha taught about the impermanent nature of life and the world. He emphasized that everything is in a constant state of change, and attachment to transient things leads to suffering.
Mindfulness and Meditation: Buddha stressed the importance of mindfulness and meditation in understanding oneself and achieving inner peace. Cultivating mindfulness helps individuals become aware of their thoughts, emotions, and sensations, leading to a deeper understanding of life.
Compassion and Kindness: Buddha taught the importance of compassion and kindness toward oneself and others. He emphasized the interconnectedness of all beings and encouraged practicing loving-kindness (Metta) and compassion (Karuna).
The Eightfold Path: Buddha presented the Eightfold Path as a guide to living a wholesome and fulfilling life. This path includes right understanding, right thought, right speech, right action, right livelihood, right effort, right mindfulness, and right concentration.
While these teachings offer insight into the nature of happiness and life, it's essential to note that Buddhism encompasses a vast body of teachings, practices, and philosophical concepts aimed at understanding the human condition and achieving liberation from suffering.