Chinese art is deeply intertwined with the philosophical and cultural traditions of China, and several key philosophies have significantly influenced the aesthetics and themes in Chinese artistic expression. Some of the prominent philosophical foundations beneath Chinese art include:
-
Confucianism:
Principles: Confucianism emphasizes ethical conduct, filial piety, and social harmony. Confucian principles have influenced Chinese art by promoting moral virtues, social order, and the expression of humanistic values in artistic creations.
Artistic Influence: Confucian ideals are reflected in art through depictions of virtuous behavior, family values, and scenes that reinforce ethical principles. Portraits of Confucian scholars and representations of benevolent rulers are common themes in Confucian-influenced art. -
Taoism:
Principles: Taoism emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao (the Way), spontaneity, and a deep connection to nature. It encourages a simple and natural way of life.
Artistic Influence: Taoist philosophy has shaped Chinese art by inspiring landscape paintings that capture the beauty of nature, often with mist-shrouded mountains, winding rivers, and solitary figures. Taoist themes of balance and the cyclical nature of existence are also reflected in art. -
Buddhism:
Principles: Buddhism, which originated in India, spread to China and brought with it a focus on spiritual enlightenment, compassion, and the impermanence of material existence.
Artistic Influence: Buddhist themes are prevalent in Chinese art, especially in sculptures, paintings, and cave art. Depictions of Buddhas, Bodhisattvas, and scenes from Buddhist narratives convey spiritual messages and a quest for enlightenment. -
Yin and Yang:
Principles: The concept of Yin and Yang represents the duality and interconnectedness of opposites. Yin is associated with receptivity, passivity, and the feminine, while Yang is associated with activity, assertiveness, and the masculine.
Artistic Influence: The Yin and Yang philosophy is reflected in the balance and harmony sought in Chinese art. Complementary elements, such as light and dark, stillness and movement, are often combined to create a sense of equilibrium. -
Five Elements (Wu Xing):
Principles: The Five Elements theory (wood, fire, earth, metal, water) is a fundamental concept in Chinese philosophy, representing the cyclical interactions and transformations in the natural world.
Artistic Influence: The Five Elements are often used symbolically in Chinese art, influencing color choices, composition, and the overall symbolism of artworks. Each element is associated with specific qualities and aspects of life. -
Harmony with Nature:
Principles: Chinese art often reflects the idea of living in harmony with nature, appreciating the beauty of the natural world, and embodying the Daoist belief in simplicity and spontaneity.
Artistic Influence: Artists strive to capture the essence of nature in various art forms, such as landscape painting and poetry. The interconnectedness of humans and nature is a recurring theme, emphasizing a holistic view of the world.
These philosophical underpinnings are not mutually exclusive, and artists often draw from multiple traditions to create works that embody a synthesis of different influences. The interplay of Confucian, Taoist, Buddhist, and other philosophical ideas has contributed to the richness and complexity of Chinese art throughout its long history.
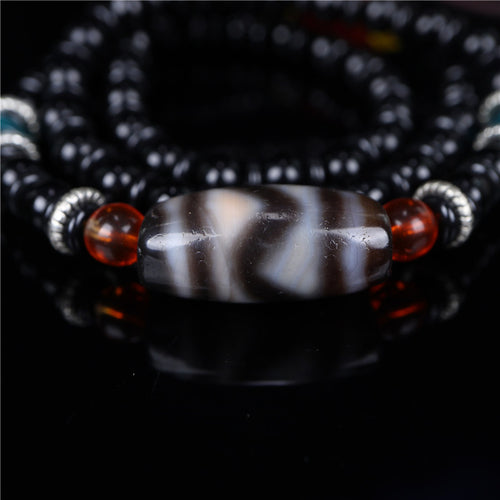
Oriental Aesthetics, the epitome of classical oriental aesthetics, aims to reshape the spiritual home of the Eastern people through the lens of aesthetics.